- Home
- Blog
- General Health
How To Treat Acne Overnight?
General Health
How To Treat Acne Overnight?
By Apollo pharmacy, Published On- 22 May 2025
Share this article
0
0 like
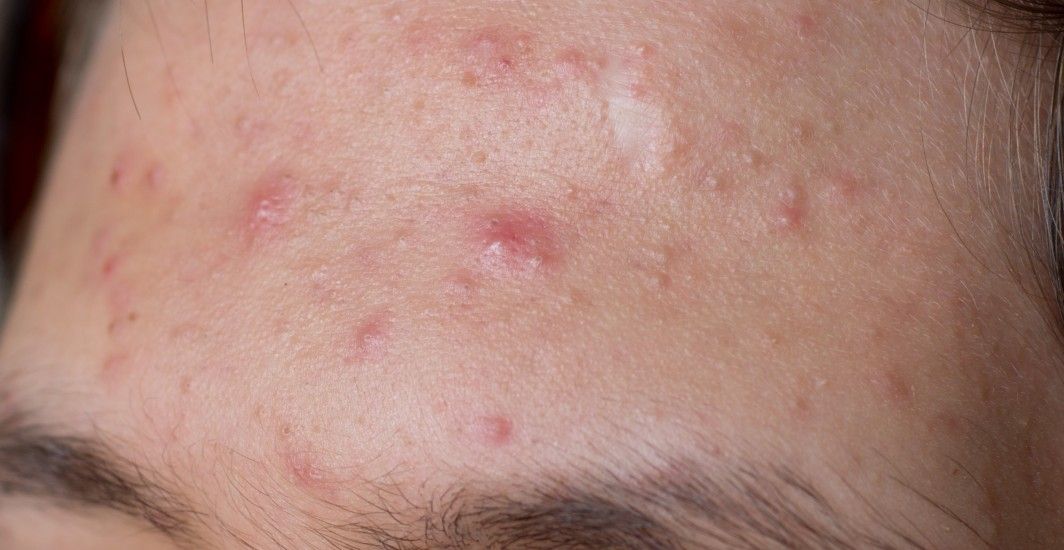
Acne is one of the most frustrating skin conditions, appearing at the worst possible times, right before a big event or an important meeting. If you're desperately searching for ways to treat acne overnight, you're not alone. While completely clearing acne in one night may not always be possible, there are proven methods to reduce redness, shrink swelling, and speed up healing. In this guide, we’ll explore fast-acting home remedies, dermatologist-approved treatments, and the role of Acnestar Gel, an effective topical solution for acne. Whether you're dealing with a sudden breakout or stubborn acne, these tips can help you wake up with clearer skin.
What is Acne?
Acne is a common chronic inflammatory skin condition that develops when hair follicles (pores) become blocked with excess oil (sebum), dead skin cells, and bacteria. This blockage leads to various types of blemishes such as blackheads, whiteheads, pimples, and in severe cases, painful nodules or cysts. Acne typically appears on areas with a high concentration of oil glands, including the face, particularly the T-zone (forehead, nose, and chin) as well as the back, chest, and shoulders. Though often associated with adolescence, acne is not limited to teenagers. Many adults in their 30s, 40s, and even later years may continue to experience breakouts, known as adult acne.
How Does Acne Form?
Before diving into treatments, it’s important to understand why acne appears suddenly. Acne develops in four key stages:
1. Excess Sebum Production
Hormones (especially androgens) stimulate oil glands to produce more sebum.
Oily skin with dead skin cells leads to clogged pores.
2. Clogged Pores (Hair Follicles)
Dead skin cells mix with sebum, blocking the pore.
This leads to blackheads (open clogged pores) or whiteheads (closed clogged pores).
3. Bacterial Growth (C. acnes)
The bacteria Cutibacterium acnes (formerly Propionibacterium acnes) thrives in clogged pores.
This triggers inflammation, leading to red, swollen pimples.
4. Inflammation & Breakouts
The body’s immune response causes redness, pus-filled pimples, or deep, painful cysts.
Types of Acne
There are many types of acne and not all of them are same. Here are the main types:
1. Non-Inflammatory Acne
Blackheads (Open Comedones): Pores clogged with oil and dead skin, open at the surface. It turns black due to oxidation.
Whiteheads (Closed Comedones): Clogged pores covered by a thin layer of skin. It appear as small, flesh-coloured bumps.
2. Inflammatory Acne
- Papules: Small, red, and tender bumps without any visible pus.
- Pustules (Pimples): Red bumps with a white or yellow centre filled with pus.
- Nodules: Large, firm, and painful lumps that form deep under the skin.
- Cysts: Deep, pus-filled, painful lesions that often lead to scarring.
What Causes Acne?
Several factors contribute to acne. Some of the common factors for acne are:
1. Hormonal Changes
- Increased androgens during puberty lead to excess oil production.
- Hormonal shifts before menstruation can cause breakouts.
- PCOS can trigger hormonal imbalances that lead to acne.
2. Genetics: A family history of acne increases your chances of developing it.
3. Bacteria & Inflammation: C. acnes bacteria thrive in clogged pores and cause inflammation.
4. Diet & Lifestyle
High-glycaemic foods like sugar and white bread may worsen acne.
- Dairy products can be a trigger for some individuals.
- Stress raises cortisol levels, leading to more oil production.
5. Skincare & Makeup Habits
- Comedogenic products can clog pores and cause acne.
- Sleeping with makeup on blocks pores and irritates the skin.
- Over-washing or harsh scrubbing can damage and inflame the skin.
Ways to Treat Acne Overnight
Since acne develops over a few days, treating it overnight requires fast-acting ingredients that reduce inflammation, kill bacteria, and unclog pores. Some of the ways to reduce acne overnight are as follows:
1. Reduce Swelling with Ice
- Gently cleanse your face and pat dry with a clean towel.
- Wrap ice cubes in a clean cloth and apply to the pimple for 5–10 minutes.
- Take a 10-minute break, then apply the ice again for another 5–10 minutes.
This can help reduce redness, swelling, and discomfort.
2. Apply an Effective Spot Treatment
- Use a benzoyl peroxide spot treatment (at least 2%) like Acnestar gel to kill bacteria and dry out the pimple.
- Apply the treatment before going to bed so it can work overnight.
3. Use a Warm Compress for Whiteheads
- Once a whitehead forms, soak a clean washcloth in warm water and apply it to the area for 10 to 15 minutes.
- Repeat 3 to 4 times a day to help the whitehead drain naturally.
4. Try Natural Remedies (Optional Alternatives)
- Green Tea: Dab cooled green tea onto the skin or use green tea-based products for anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial benefits.
- Tea Tree Oil: Dilute with a carrier oil (like jojoba or coconut oil) and apply a tiny amount to pimples.
- Copaiba Oil: Use a topical gel with copaiba extract to help calm inflammation and prevent new pimples.
- Mineral Clays: Apply a clay mask (like kaolin or Dead Sea mud) to absorb oil and reduce bacteria.
5. Avoid These Common Mistakes
- Toothpaste: Modern toothpaste does not help acne and may irritate the skin.
- Scrubbing: Harsh scrubbing can worsen acne. Always wash gently.
- Tanning: Tanning does not treat acne and increases the risk of skin damage.
- Popping Pimples: Can lead to scarring, infection, and worsen inflammation.
When to See a Dermatologist?
If your acne is persistent or severe, consider professional treatments such as:
- Topical medications: Salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, retinoids, or antibiotics
- Oral medications: Retinoids, antibiotics, or hormonal treatments (e.g., birth control pills).
- Professional advice: Stick with any new acne treatment for at least 6–8 weeks before switching.
For quick fixes, Acnestar Gel remains a reliable over-the-counter option as recommended by dermatologists.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Overnight Breakouts
While emergency treatments help, preventing acne requires long-term care. Some of the lifestyle changes that can help prevent acne are as follows:
- Cleanse your face twice daily: Using a gentle cleanser—avoid over-washing, as it can strip the skin of natural oils and cause irritation.
- Use a non-comedogenic moisturiser: To keep your skin hydrated without blocking pores. Even oily skin needs proper moisture.
- Change your pillowcases at least once a week: To reduce the accumulation of bacteria, oil, and dead skin cells that can lead to breakouts.
- Keep your hands away from your face: To prevent the transfer of dirt, oil, and bacteria that can clog pores.
- Stay well-hydrated: By drinking plenty of water throughout the day—this supports healthy skin and helps flush out toxins.
- Limit your intake of sugar and dairy products: These may contribute to breakouts in some individuals.
Conclusion
Acne can be a persistent and confidence-shaking condition, but with the right care, it can be effectively managed- even overnight. While not all breakouts can disappear in a single night, targeted treatments such as ice therapy, spot applications, and gentle skincare can significantly reduce inflammation and swelling. Incorporating trusted solutions like Acnestar Gel into your night-time routine may help combat bacteria and speed up healing. Alongside these quick remedies, adopting healthy lifestyle habits is essential for long-term prevention. Staying consistent with skincare, avoiding common mistakes, and knowing when to seek professional advice can make a big difference. Remember, patience and the right approach are key to clearer, healthier skin. With dedication and the right products, you can regain control over your skin and feel more confident in your daily life.
Services
General Health
Leave Comment
Services
Recommended for you

General Health
Ingredients To Look For While Buying Skincare Products?
Discover the key ingredients to look for when purchasing skincare products. Learn about new technologies, guidelines, and lifestyle factors that can help you make informed choices for healthier skin.

General Health
Surzole Antifungal Cream: Uses, Application, and Effectiveness
Surzole Antifungal Cream is an effective topical treatment for fungal skin infections, including Athlete's foot. Learn about its uses, how to apply it, and its benefits for clear, healthy skin.

General Health
C- Reactive Protein (CRP) Test: Readings And Ways To Lower It
Learn about CRP, a protein produced by the liver in response to inflammation. Discover its role in diagnosing and monitoring diseases like infections, autoimmune disorders, and cardiovascular conditions. Stay informed about the latest guidelines, technologies, and lifestyle factors related to CRP.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
