- Home
- Health Condition
Medicine For Cystitis
Medicine For Cystitis
- Total Items (9)
 RX
RXMartifur MR 100 Tablet 10's
₹190.80
MRP ₹212
10% off

Utikit Capsule 10's
₹430.20
MRP ₹478
10% off
 RX
RXMartifur Tablet 14's
₹78.30
MRP ₹89
12% off

Cital-UTI XL Sugar Free Suspension 200 ml
₹289.80
MRP ₹322
10% off
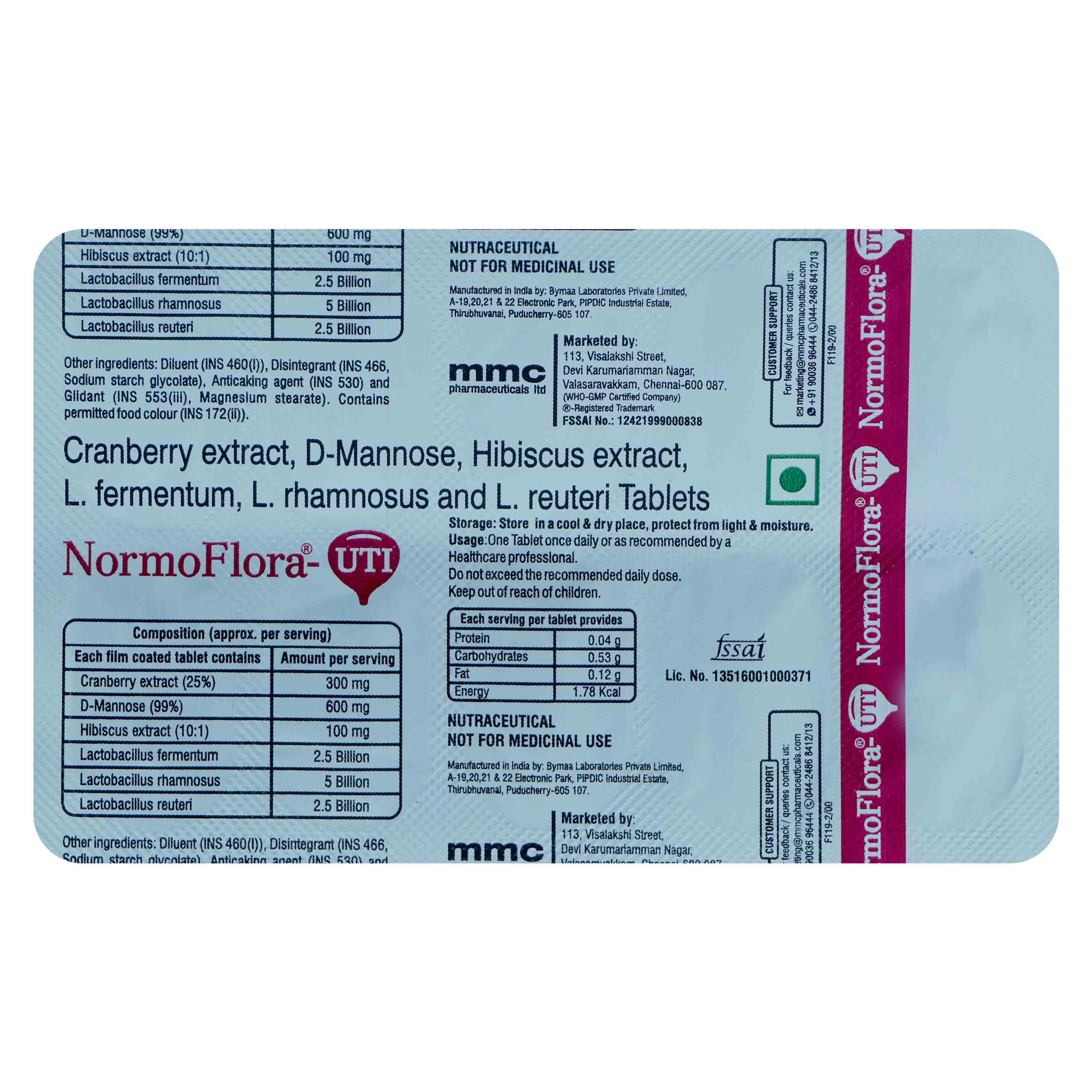
Normoflora-UTI Tablet 10's
₹387
MRP ₹430
10% off
 RX
RXMartifer 100 mg Tablet 10's
₹80.10
MRP ₹89
10% off

Shelgut Pro Sachet 2gm
₹34.20
MRP ₹38
10% off

Utrofiz Sugar Free Orange Flavour Powder Sachet 5 gm
₹49.50
MRP ₹55
10% off

Alkapac Adult Sachet 5 gm
₹34.20
MRP ₹38
10% off
Medicine For Cystitis
Cystitis is a common condition characterised by inflammation of the bladder, often caused by bacterial infections. It is a type of urinary tract infection (UTI) that can lead to symptoms such as frequent urination, pain or burning during urination, and abdominal discomfort. While mild cases may resolve on their own, medicines are often required to treat bacterial cystitis effectively and prevent complications. This guide explores the types of medicines used for cystitis, their benefits, dosage instructions, and where you can obtain these medications conveniently.
Types of Medicine for Cystitis
Treatment typically involves medications that target the cause of the infection, reduce symptoms, and help prevent recurrence. Below is an overview of the different types of medicines used to manage cystitis:
1. Antibiotics for Bacterial Cystitis
Antibiotics are the first-line treatment for bacterial cystitis. These medications work by targeting and killing the bacteria responsible for the infection, helping to clear up the condition.
- Nitrofurantoin: Often prescribed for uncomplicated bladder infections, it works by disrupting bacterial metabolism.
- Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole: A commonly used combination of antibiotics that effectively treat UTIs, including cystitis.
- Amoxicillin & Amoxicillin-Clavulanate: These antibiotics target specific bacteria, providing effective treatment for bladder infections.
- Ciprofloxacin & Levofloxacin: Typically used for more severe or recurrent infections, these fluoroquinolones are effective against a wide range of bacterial pathogens.
- Fosfomycin: A single-dose antibiotic used to treat uncomplicated cystitis by interfering with bacterial cell wall synthesis.
2. Pain Relievers (Urinary Analgesics)
Pain relievers help manage the discomfort, burning sensation, and irritation caused by cystitis. These medications do not treat the infection but provide relief from the painful symptoms.
- Phenazopyridine: A commonly used urinary analgesic that temporarily numbs the urinary tract lining, offering relief from burning and discomfort during urination.
3. Antifungal Medications
In cases where cystitis is caused by fungal infections (such as yeast infections), antifungal medications are prescribed to target and eliminate the fungal pathogens.
- Fluconazole: This oral antifungal is often used to treat fungal infections in the urinary tract, including those that cause cystitis.
- Amphotericin B: Typically administered intravenously for more severe or systemic fungal infections, including those that affect the urinary tract.
4. Alkalizing Agents
Alkalizing agents help neutralize the acidity of urine, which can provide relief from the burning sensation during urination that often accompanies cystitis.
- Sodium Bicarbonate-Based Products: These medications are commonly used to raise the pH of urine, reducing its acidity and alleviating the discomfort associated with cystitis.
5. Hormonal Treatments for Postmenopausal Women
For postmenopausal women, vaginal estrogen therapy may be used to help strengthen the lining of the bladder and urinary tract, reducing the likelihood of recurrent cystitis. This treatment can improve the health of the tissues in the urinary tract and minimise irritation or infection.
6. Other Supportive Treatments
In addition to the primary treatments, several other supportive therapies may be used to manage cystitis and reduce recurrence:
- Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce bladder inflammation and relieve discomfort in cases of non-infectious cystitis or chronic bladder conditions.
- Probiotics: These are sometimes recommended to help maintain urinary tract health and balance the gut microbiome. Probiotics can help reduce the recurrence of UTIs and cystitis, particularly in individuals prone to frequent infections.
Benefits of Using Medicine for Cystitis
Using the right medicine for cystitis offers multiple benefits for those dealing with the condition:
- Rapid Relief from Symptoms: Antibiotics and pain relievers help relieve the burning, pain, and discomfort associated with cystitis, allowing you to feel better more quickly.
- Prevention of Recurrence: Proper use of medicine for cystitis, especially antibiotics, can help reduce the risk of recurrent infections, which is a common problem for individuals with frequent urinary tract infections.
- Targeted Treatment: Antibiotics directly address the underlying cause of cystitis, while pain relievers and antispasmodics focus on alleviating specific symptoms.
- Improved Quality of Life: Effective treatment improves day-to-day comfort, allowing you to manage cystitis more easily and continue with your regular activities.
Dosage & Usage Instructions of Medicine for Cystitis
Following the prescribed dosage and instructions is crucial when using medicine for cystitis. Here’s a general guide on how to use these medications:
Antibiotics:
- Dosage: Antibiotics are typically taken for 3-7 days, depending on the medication and the severity of the infection.
- Usage Instructions: It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if you start feeling better, to prevent the infection from returning.
Pain Relief Medications:
- Dosage: Medicines like phenazopyridine are often taken 2-3 times per day for up to 2 days. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen are typically taken as needed to relieve discomfort.
- Usage Instructions: Use pain relief medications only for short-term symptom management. If symptoms persist, consult your healthcare provider.
Antispasmodics:
- Dosage: Antispasmodic medications like oxybutynin are typically taken 1-2 times daily, depending on the severity of your symptoms.
- Usage Instructions: Follow your healthcare provider's instructions and adjust the dosage as needed for symptom control.
Antifungal Medications
- Dosage: For fungal cystitis, medications like fluconazole are often taken once daily. In severe cases, amphotericin B may be administered intravenously in a hospital setting.
- Usage Instructions: Follow the exact dosage and duration prescribed by your doctor. Do not discontinue antifungal treatments prematurely, as this may lead to treatment failure or recurrence.
Alkalizing Agents (Urinary Softeners)
- Dosage: Sodium bicarbonate-based medications are usually taken 2-3 times daily, depending on the severity of urinary acidity.
- Usage Instructions: Dissolve the recommended dose in water and drink as directed. Avoid overuse, as excessive alkalisation may lead to side effects.
Hormonal Treatments
- Dosage: Vaginal estrogen creams or tablets are typically applied once daily initially, then reduced to a few times per week as maintenance therapy.
- Usage Instructions: Follow your doctor’s recommendations for the frequency and duration of use. Ensure proper hygiene when applying the cream or inserting the tablet.
Where to Buy Medicine for Cystitis Online
If you're looking for treatments for cystitis, such as antibiotics or pain relievers, you can conveniently order them online through trusted platforms like Apollo 24|7. With just a few clicks, you can have your medications delivered directly to your doorstep. For personalised treatments, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider. With doctor consultations and lab tests also available on the app, we provide complete solutions — all in one place.
Frequently asked questions
Mild cystitis may resolve on its own, but treatment with medicine for cystitis is usually necessary to relieve symptoms and prevent complications.
If you miss a dose of your antibiotic, take it as soon as you remember. If it's almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and take the next one at the usual time. Never take two doses at once.
Some antibiotics may cause side effects like nausea, diarrhoea, or allergic reactions. Pain relief medications like phenazopyridine may turn your urine orange. Always consult your doctor if you experience side effects.
Antibiotics typically start working within a day or two, while pain relief medications provide immediate relief from symptoms. Complete relief may take a few days.
Yes, cystitis can recur, especially in individuals with frequent urinary tract infections. Following your doctor’s recommendations and taking prescribed medications as directed can help prevent recurrence.
