Medicine For Urine Infection
- Total Items (0)
 RX
RXMartifur MR 100 Tablet 10's
₹190.80
MRP ₹212
10% off

Utikit Capsule 10's
₹430.20
MRP ₹478
10% off
 RX
RXMartifur Tablet 14's
₹78.30
MRP ₹89
12% off

Cital-UTI XL Sugar Free Suspension 200 ml
₹289.80
MRP ₹322
10% off
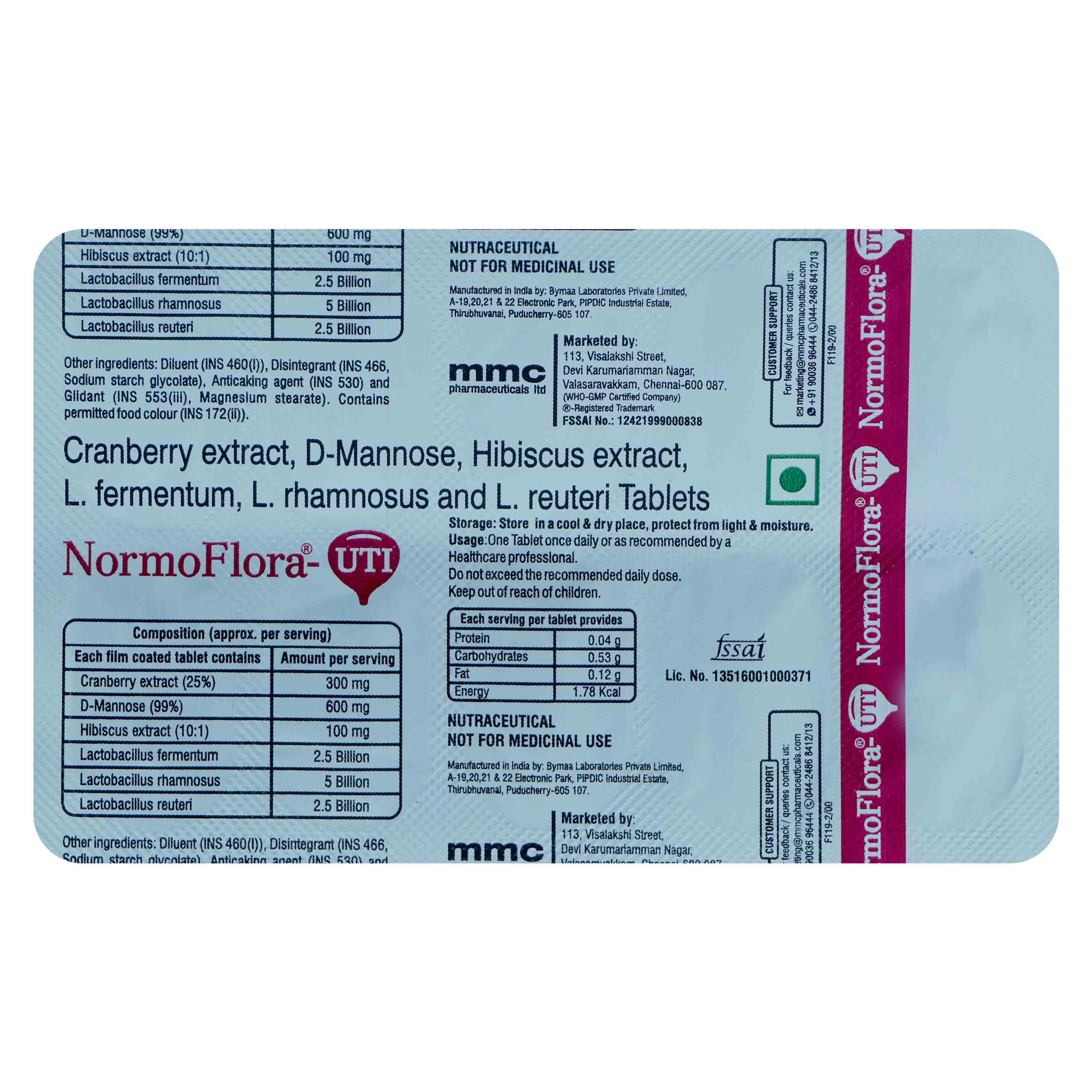
Normoflora-UTI Tablet 10's
₹387
MRP ₹430
10% off
 RX
RXMartifer 100 mg Tablet 10's
₹80.10
MRP ₹89
10% off

Shelgut Pro Sachet 2gm
₹34.20
MRP ₹38
10% off
Medicine for urine infection
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common bacterial infections that affect the urinary system, including the bladder, kidneys, and urethra. They can cause symptoms such as frequent urination, burning sensations, and lower abdominal discomfort. UTIs are more prevalent in women but can affect individuals of all ages and genders. Early treatment is necessary to prevent complications, including kidney infection or repeated UTIs. Pharmaceutical treatments for UTIs are designed to target and eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. The mainstay of UTI treatment is antibiotics, whose action is either killing the bacteria or inhibiting the growth of the bacteria. Depending on the type of infection, the severity, and the individual's health status, different antibiotics and dosage regimens may be prescribed.
This guide provides an overview of the various medications used to treat UTIs, their mechanisms of action, recommended dosages, potential side effects, and safety precautions. Understanding these treatment options will help you make informed decisions about managing a urinary tract infection effectively.
Types of Medicines Used for Urine Infection
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common infections affecting various parts of the urinary system, and they are usually treated with antibiotics to eliminate the bacteria responsible for the infection. The selection of the appropriate medication depends on factors such as the infection's severity, the causative microorganism, and patient factors such as age, health status, and potential drug allergies. This guide highlights the primary classes of medications used to treat UTIs.
1. Antibiotics
Antibiotics are the primary therapy for UTIs, aiming to eliminate bacterial pathogens. Common antibiotics include:
- Nitrofurantoin: Often prescribed for uncomplicated bladder infections (cystitis) and is well-tolerated.
- Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole: A combination antibiotic commonly used for UTIs caused by E. coli.
- Ciprofloxacin: A fluoroquinolone antibiotic used for more complicated infections or kidney infections (pyelonephritis).
- Amoxicillin: A penicillin-based antibiotic used for treating uncomplicated UTIs, especially in pregnant women or children.
- Cephalosporins: Broad-spectrum antibiotics that are used when other treatments fail or when antibiotic resistance is a concern.
2. Urinary Analgesics
Medications like Phenazopyridine are used for symptomatic relief. This drug helps alleviate discomfort, burning, and urgency associated with UTIs by numbing the urinary tract, although it does not treat the underlying infection.
3. Probiotics
Lactobacillus supplements may be recommended for preventing recurrent UTIs, particularly after antibiotic treatment, by restoring the natural flora of the urinary tract and promoting a healthy microbial balance.
Benefits of Using Medicine for Urine Infection
Medications play a crucial role in the effective management of UTIs, providing numerous benefits to patients.
- Symptom Relief: Antibiotics are the primary treatment for UTIs, helping to eliminate the bacteria responsible for the infection. This reduces symptoms like painful urination, urgency, and pelvic discomfort. Urinary analgesics, such as Phenazopyridine, provide additional relief from burning sensations and discomfort while the infection is being treated.
- Prevention of Complications: UTIs, if left untreated, can develop into more serious complications: kidney infections or sepsis. Antibiotics help prevent the infection from spreading to the kidneys, minimising the risk of long-term damage or hospitalisation.
- Faster Recovery: Proper medication accelerates recovery by targeting the root cause of the infection, allowing patients to return to their normal activities more quickly and with fewer disruptions.
- Reduced Risk of Recurrence: Probiotics and other preventive medications may help restore healthy bacteria in the urinary tract, reducing the chances of recurrent infections, particularly in individuals prone to frequent UTIs.
- By effectively treating the infection, medications help relieve symptoms, prevent complications, and support faster recovery. Always consult a healthcare provider for appropriate treatment.
Dosage & Usage Instructions of Medicine for Urine Infection
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are commonly treated with antibiotics. Below are general guidelines for dosage and usage:
How much to take:
- Dosage varies by medicine and infection severity.
- Typically, for antibiotics like Trimethoprim (100-200mg twice daily) or Nitrofurantoin (50-100mg 2-4 times daily), follow the doctor's prescription.
When to take:
- Take as prescribed, usually once or twice a day.
- For best results, take with or after meals to reduce stomach upset.
When to stop:
- Complete the full prescribed course, even if symptoms improve, typically 3-7 days.
- Do not stop early without consulting your healthcare provider.
Caution :
- Avoid alcohol with some antibiotics (e.g., Metronidazole).
- Inform your doctor about allergies or kidney issues.
- Monitor for side effects like nausea or diarrhoea.
Where to Order Medicine for Urine Infection Online?
Shopping for medicine for urine infection online can be a convenient and efficient way to get the relief you need quickly. Platforms like Apollo 24|7 offer a wide range of OTC medications that can be delivered right to your doorstep. When shopping online, ensure that you are purchasing from a reputable source to guarantee the authenticity and quality of the medication. Make a commitment to your well-being by opting for reputable sources like Apollo 24|7, which prioritise safety and quality.
Frequently asked questions
Preventative measures include drinking plenty of water, urinating after sexual activity, and avoiding irritating feminine products. Your doctor may recommend low-dose antibiotics if UTIs are recurrent.
Over-the-counter products like cranberry supplements or Phenazopyridine (a pain reliever for UTIs) can provide temporary relief but do not treat the underlying infection. Always consult your doctor for proper antibiotic treatment.
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhoea, headache, and stomach upset. Severe reactions may include allergic reactions or kidney issues. Contact your doctor if you experience any unusual symptoms.
Probiotics may help restore the balance of good bacteria in the body after a course of antibiotics, reducing the risk of yeast infections or gastrointestinal upset. However, they should not replace prescribed antibiotics for UTI treatment.
Yes, if the infection spreads to the kidneys, it can cause pain in the lower back or flanks. Seek medical attention if you experience severe pain, fever, or vomiting alongside your UTI symptoms.
