
Ovulation is the phase in the menstrual cycle when an egg is released from the ovary, ready for potential fertilisation. Understanding ovulation helps you better understand your body and plan your pregnancy.
The menstrual cycle is a natural monthly process that prepares the body for possible pregnancy. It typically lasts 28-30 days. Understanding the menstrual cycle can help you track your fertility and maintain your reproductive health.

The menstrual cycle includes four phases, each playing a unique role in preparing the body for a potential pregnancy.
Ovulation is the release of a mature egg from the ovary, indicating peak fertility. Let's examine how you can track your ovulation phase to get pregnant faster.

For most people, the timing of ovulation after their period depends on their cycle length.
Understand your ovulation signs to boost your chances of pregnancy. Here’s what to look out for:

Fertility is highest on ovulation day and up to 24 hours after. Symptoms to track ovulation include
Using an ovulation test kit can help identify your most fertile days.

It’s best to start testing a few days before the expected ovulation date, which is usually mid-cycle. A positive ovulation test indicates that ovulation will likely occur at or after 24-36 hours.
Recognising ovulation symptoms can help identify peak fertility days.
Recognising ovulation symptoms can help identify peak fertility days. Some common symptoms include increased cervical mucus, mild abdominal pain, increased basal body temperature, breast tenderness, bloating, spotting, and slight pain or cramping.
This mild, one-sided abdominal discomfort happens as the ovary releases an egg. While generally harmless, ovulation pain can be a helpful indicator of peak fertility timing.
During ovulation, you may notice changes in cervical mucus, often called ovulation discharge. Typical signs of ovulation discharge include a clear, stretchy texture, which signals peak fertility.
Ovulation usually lasts 12-24 hours when the egg travels down the fallopian tube. This marks the brief period when an egg is viable for fertilisation.
Massage Helps
Massaging the head, ears and foot with oil post-menstruation helps to stimulate ovulation

Nasya Helps
Herbal oil drop installation in the nose can help in ovulation stimulation.

Healthy weight
Reduce ovulation risks caused by being too heavy or too light by maintaining your weight.

Nutritious diet
Eat leafy greens, citrus fruits, and pulses rich in folic acid for baby’s neural growth.

Ovulation guide
During your ovulation, having a thin and stretchy discharge like a raw egg white is normal.

Ovulation kit
Using an ovulation kit helps identify your most fertile days to boost pregnancy chances
Cycle tracking
A menstrual cycle log helps you identify the best time for intercourse to conceive.

Discover trusted advice from experts for all stages of your parenting
Stay on top of your health! Check out the recommended tests and scans you need before getting pregnant.
Ovulation typically occurs around day 14 in a 28-day cycle, but this can vary widely among women.
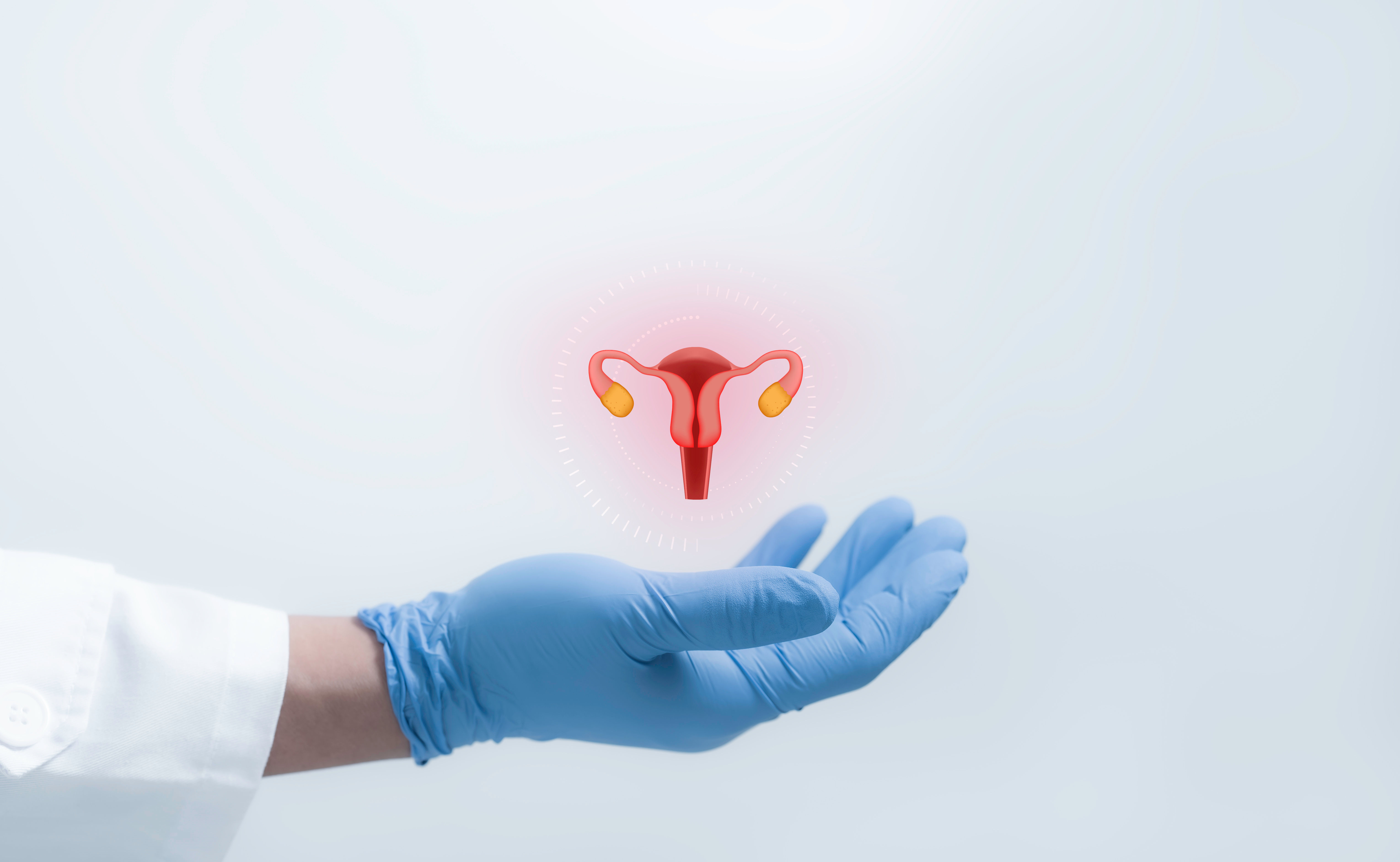
Ovulation is the release of a mature egg from the ovary. The egg then travels to the fallopian tube, where it may meet sperm and become fertilised.
If ovulation does not occur, pregnancy is not possible. Various factors, including hormonal imbalances like PCOS, thyroid disorders, weight gain, stressors, and medical conditions, can disrupt ovulation.
Physical signs, such as changes in cervical mucus, mild abdominal pain, and increased basal body temperature, can help identify ovulation.
The fertile window lasts about 12-24 hours after ovulation. However, since sperm can live up to five days, the days leading up to ovulation are also fertile.
If fertilisation does not occur, the egg disintegrates, and the body prepares to shed the uterine lining in the next menstrual cycle. If fertilised, the egg implants in the uterine lining, and pregnancy may occur.