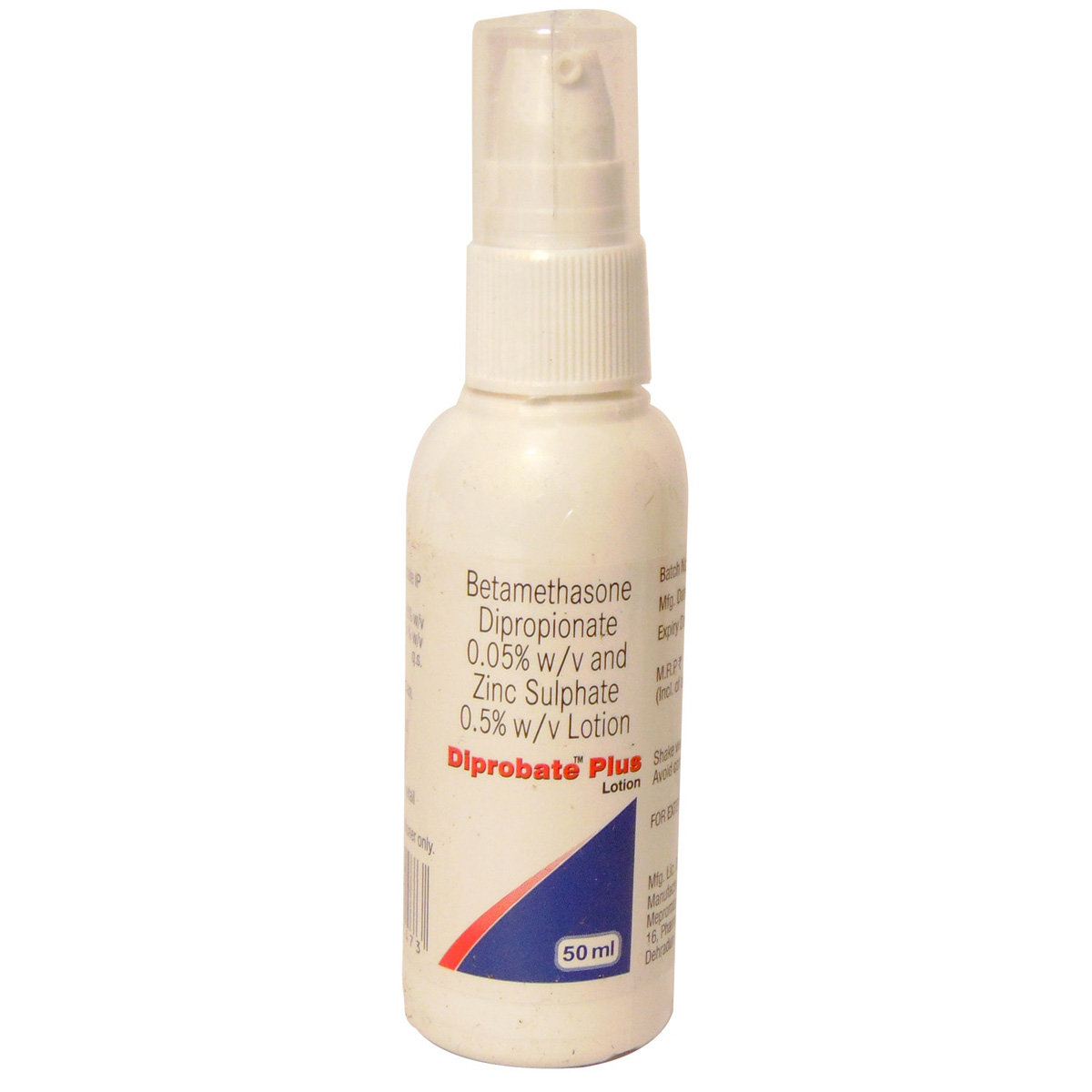
Betamethasone+zinc
About Betamethasone+zinc
Betamethasone+zinc is used to treat eczema, contact dermatitis and psoriasis. Eczema is a condition in which the skin becomes red, itchy, and inflamed due to external agents such as soaps, dyes, or other irritants. Psoriasis is a skin disorder in which the skin becomes scaly, swollen, and itchy.
Betamethasone+zinc contains Betamethasone and Zinc, which block the production of chemical messengers that cause inflammation. It also acts as an antiseptic (prevents microbes' growth) and astringent (contracts the skin cells) on the skin.
You should use this medicine exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Common side effects of Betamethasone+zinc include redness, inflamed hair follicles, itching, and blistering at the application site. If any of these side effects persist or get worse, inform your doctor immediately.
It is not recommended to use Betamethasone+zinc if you are allergic to any of its contents. Consult your doctor if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Betamethasone+zinc is not recommended for use in children below 13 years of age. Betamethasone+zinc should be used with caution in elderly patients.
Uses of Betamethasone+zinc
Medicinal Benefits
For Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis):
- Helps reduce redness, swelling, and itching of the affected skin.
- Provides soothing relief and improves skin comfort.
For Contact Dermatitis:
- Relieves inflammation and irritation caused by allergens or irritants.
- Helps calm the skin and supports faster recovery.
For Psoriasis:
- Reduces redness, itching, and discomfort associated with psoriatic lesions.
- Helps improve the appearance and texture of affected skin.
Directions for Use
- Betamethasone+zinc is for external use only.
- It is usually applied 1-2 times daily or as directed by your doctor.
- Check the label for directions before using this medicine.
- Gently rinse the affected area with saline or water before applying Betamethasone+zinc. Pat the skin and dry it with a clean cotton towel. Apply a generous amount of Betamethasone+zinc and spread it evenly on the affected areas of the skin to form a 1/8-inch thick layer with clean and dry hands. You can also apply Betamethasone+zinc with a piece of clean cotton wool or gauze swab.
- Wash your hands before and after using Betamethasone+zinc unless the treatment is for hands.
- If Betamethasone+zinc accidentally comes into contact with the nose, mouth, or eyes, rinse with water thoroughly.
Storage
Side Effects of Betamethasone+zinc
- Redness at the application site
- Inflamed hair follicles
- Itching
- Blistering
Drug Warnings
- Do not use Betamethasone+zinc if you are allergic to any of its components.
- If the medicine accidentally gets into your eyes, nose, mouth, or genitals, rinse with water thoroughly.
- Inform your doctor immediately if you notice swelling or weight gain around the trunk or in the face, as it may be a sign of Cushing’s syndrome (high levels of cortisol in the body).
- Please do not use this medicine for longer than recommended by your doctor, as it may suppress adrenal gland function and may increase the risk of vision problems.
- Betamethasone+zinc should be used with caution in patients with diabetes as it can increase blood glucose levels.
- It would be best if you did not cover the treated area with a bandage or plaster, especially the face, without checking with your doctor.
Drug Interactions
Drug-Drug Interactions: No interactions found.
Drug-Food Interactions: No interactions found.
Drug-Disease Interactions: No interactions found.
Drug-Drug Interactions Checker List:
Safety Advice

Alcohol
safe if prescribedBetamethasone+zinc may not interact with alcohol.

Pregnancy
cautionBetamethasone+zinc is a Category C pregnancy drug and may cause harmful effects on the unborn baby. So, it is given to a pregnant woman only if the doctor thinks the benefits outweigh the risks.

Breast Feeding
cautionBetamethasone+zinc may pass into breastmilk and cause harmful effects in the nursing baby. So, it is given to a breastfeeding mother only if the doctor thinks the benefits outweigh the risks.

Driving
safe if prescribedBetamethasone+zinc may not affect your ability to drive.

Liver
cautionBetamethasone+zinc should be used with caution in patients with liver diseases. The dose may have to be adjusted by your doctor.

Kidney
cautionBetamethasone+zinc should be used with caution in patients with kidney diseases. The dose may have to be adjusted by your doctor.

Children
unsafeBetamethasone+zinc is not recommended for children below 13 years as there is a risk of growth retardation.
Habit Forming
Diet & Lifestyle Advise
Skin Care Practices:
- Use mild soap while bathing and prefer warm water instead of hot water.
- Avoid harsh skincare products that may irritate the skin.
- Do not scratch or pick the skin to prevent infection of the affected area.
Lifestyle & Stress Management:
- Manage stress through healthy routines to help reduce flare-ups.
- Exercise regularly and get plenty of sleep to support skin healing.
Diet & Hydration:
- Eat a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats, and fish.
- Drink plenty of water to keep the skin well hydrated.
- Avoid foods high in sugar as they may increase inflammation.
Allergy & Irritant Avoidance:
- Limit intake of allergy-triggering foods such as dairy products, soy, eggs, and nuts.
- Avoid contact with harsh soaps, detergents, and rough fabrics that can irritate the skin.
Special Advise
- If applied to the eyelids, care is needed to ensure that the preparation does not enter the eye, as cataract and glaucoma might result from repeated exposure.
- Do not apply to open and cut wounds.
Patients Concern
Disease/Condition Glossary
Eczema: Eczema is also known as atopic dermatitis. It is a skin inflammatory condition characterized by red and itchy rashes. The most common cause of eczema is allergies. Contact with soaps, dyes, chemicals or other irritants may trigger rashes. Avoiding the triggers helps to prevent flare-ups of eczema.
Contact dermatitis: Contact dermatitis is when the skin becomes red and inflamed after it comes in contact with any allergens (causes allergy or irritation). Symptoms include dry, itchy or swollen skin.
Psoriasis: Psoriasis is an autoimmune skin disease characterised by red, itchy and scaly rashes. This condition occurs when skin cells grow and build up rapidly, resulting in scaly rashes. It is a chronic disease and doesn’t have a permanent cure. So, to avoid flare-ups of the disease, avoid triggers such as stress and cold.
FAQs
Betamethasone+zinc is used to treat eczema, contact dermatitis‚ and psoriasis.
Betamethasone+zinc contains Betamethasone and Zinc, which block the production of chemical messengers that cause inflammation. It also acts as an antiseptic (prevents microbes' growth) and astringent (contracts the skin cells) on the skin.
Betamethasone+zinc is for topical use (for skin) only. Do not use Betamethasone+zinc on the face and avoid contact with eyes, nose, mouth and genitals. Do not put a bandage or a dressing on the affected area while using Betamethasone+zinc unless advised by the doctor. Please do not use it on larger areas and for prolonged periods unless prescribed by the doctor.
The common side-effects of Betamethasone+zinc are redness, inflamed hair follicles, itching, and blistering at the application site. These side effects are usually mild and temporary. However, if any of these side effects persist or get worse, inform your doctor immediately.
Inform your doctor before using any medications while using Betamethasone+zinc. If the doctor prescribes other skin creams or ointments along with Betamethasone+zinc, you should maintain an interval of at least 30 min between the two medications.
Betamethasone+zinc is not recommended to treat diaper rash or redness. However, please consult a doctor before using Betamethasone+zinc in children.
Betamethasone+zinc is used on the hair if the individuals have conditions like psoriasis, eczema, and dermatitis, but only when the doctor suggests using it. Apply it on the hair after washing and drying your scalp correctly. Consult a doctor if you have any concerns for personalized guidance.
The use of Betamethasone+zinc, containing Betamethasone and Zinc, is contraindicated in certain situations, emphasizing the importance of caution and medical guidance. Specifically, individuals with known allergies, pregnant or breastfeeding women, and those with infected skin should avoid using Betamethasone+zinc unless advised by a doctor. Additionally, it is crucial to inform your doctor about other medications you are taking and to check with them before undergoing any cosmetic treatments while using Betamethasone+zinc. Following these guidelines and consulting with a doctor can ensure the safe and effective use of Betamethasone+zinc and achieve optimal results.
Gently rinse the affected area with saline or water before applying Betamethasone+zinc. Pat the skin and dry it with a clean cotton towel. Apply a generous amount of Betamethasone+zinc and spread it evenly on the affected areas of the skin to form a 1/8-inch thick layer with clean and dry hands. You can also apply Betamethasone+zinc with a clean cotton wool or gauze swab. Wash your hands before and after using Betamethasone+zinc unless the treatment is for hands.
Do not stop taking Betamethasone+zinc even after your symptoms are relieved. Completing the recommended course is essential to having full benefits. Stopping suddenly can lead to the reactivation of your infection or cause side effects. Instead, consult your doctor and inform them about your progress. They will assess your status and provide suitable guidance to avoid adverse complications in your health status.
Using Betamethasone+zinc in higher doses or for extended periods may cause negative health complications or worsen your symptoms. Always follow your doctor's instructions carefully, please don’t take more than the recommended dose and duration.
Store Betamethasone+zinc in its original container, keeping it cool, dry, and out of sunlight. Keep it out of the reach of children. Regularly check the expiration date. When you need to dispose of the medicine, remove the label, place it in a plastic bag, and throw it away in the household trash. Remember, never flush the medicine down the toilet or sink to prevent harm to others and the environment.